Opportunity and challenge: Carbon dioxide emission ranking of Chinese cities
- By Zhou Muzhi
 0 Comment(s)
0 Comment(s) Print
Print E-mail China.org.cn, February 17, 2023
E-mail China.org.cn, February 17, 2023
Editor's note: At a time when carbon peak and neutrality goals have become one of the most important national strategies, all cities are looking for their own paths to it. Cloud River Urban Research Institute released a carbon dioxide emission ranking of Chinese cities based on the latest results of satellite data parsing and geographic information system (GIS) analysis, and Professor Zhou Muzhi, head of the institute, provided Chinese cities an exhaustive "physical examination report" on carbon peak and neutrality strategy by making a category-based analysis of the top 30 emitting Chinese cities.
In 2022, the Russia-Ukraine conflict interrupted global energy supply, as the global coal output abruptly rocketed to a record high of 8 billion metric tons, and the global carbon dioxide emissions also set a new record. At the same time, the development of new energy and new energy vehicles as well as other efforts to reduce carbon emissions are becoming new engines for global scientific and technological and economic progress. A lot of new unicorns in the world last year came from the new energy sector. In Guangdong province in southern China, unicorns in the new energy sector account for nearly 50% of the province's total new unicorns. New energy vehicles are even more popular. As early as 2020, Tesla surpassed Toyota to become the world's largest auto maker by market value. BYD surpassed Volkswagen in June last year to become the world's third largest auto maker by market value. How to pursue high-quality development through energy conservation and emission reduction has become a challenge facing Chinese cities.
1. Carbon dioxide emission ranking of Chinese cities
The 297 cities at the prefectural level and above in China are home to 94.7% of the country's population and produce 96.6% of its GDP. Therefore, an analysis of their carbon emissions is vital to truly understand China's carbon dioxide emissions and seek paths to carbon peak and neutrality.
China Integrated City Index compiled by Cloud River Urban Research Institute offers a multidimensional perspective of and insights into the development of all the 297 cities through a multimodal index analysis based on data resources in different fields, including statistical data, big data, and satellite remote sensing data, elevating the research on metropolises to a new level. The institute has also found ways to accurately calculate carbon dioxide emissions of cities through satellite data parsing and GIS analysis, thus enabling a comprehensive and profound analysis of cities' emissions.
By monitoring and evaluating carbon emissions of the 297 cities, China Integrated City Index unveiled the top 30 emitting Chinese cities in the pre-pandemic year 2019, as shown in Figure 1. The top 10 cities were Shanghai, Beijing, Tianjin, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Tangshan, Harbin, Ningbo, Qingdao, and Chongqing. Their combined carbon emissions accounted for 16.2% of the national total, 1.1 times that of Russia, the world's fourth largest emitter, and 1.6 times that of Japan, the world's fifth largest emitter.
Those ranking 11th to 30th were Dongguan, Wuxi, Jinan, Zhengzhou, Xuzhou, Taizhou, Changchun, Zaozhuang, Zhangjiakou, Taiyuan, Baoding, Ordos, Wuhan, Daqing, Nantong, Xi'an, Nanjing, Hohhot, Hangzhou, and Shenzhen.
The total carbon emissions of all the 30 cities made up for 32.6% of the country's total, 1.3 times that of India, the world's third largest emitter. That is precisely why an analysis of their carbon emissions matters a lot.
Figure 1 Top 30 Chinese cities in terms of carbon emissions in 2019

Source: China Integrated City Index 2020 by Cloud River Urban Research Institute
2. Category-based analysis of top 30 emitting cities
The top 30 emitting cities in China fall into three categories — first, central cities, including municipalities directly under the central government, provincial capitals, and cities specifically designated in the state plan; second, coastal cities with a developed manufacturing sector; third, oil/coal producing cities or cities with developed energy/heavy chemical industries that emit a large amount of carbon dioxide, such as power, and iron and steel. Some cities may fit into more than one category. For example, Shanghai is not only a central city, but also a coastal city with developed manufacturing sector and sizeable energy/heavy chemical industries.
(1) Central cities
There are 36 central cities in China, among which 18 were in the top 30 emitters, namely Shanghai, Beijing, Tianjin, Guangzhou, Harbin, Ningbo, Qingdao, Chongqing, Jinan, Zhengzhou, Changchun, Taiyuan, Wuhan, Xi'an, Nanjing, Hohhot, Hangzhou, and Shenzhen. As economic hubs with a large population and places with high standards of living, these central cities are responsible for a large proportion of the country's carbon emissions.
The aggregate carbon emissions of the aforementioned 18 central cities accounted for 22.2% of the country's total, and for all the 36 core cities, the percentage was as high as 30.3%. In this sense, the key for China to achieving carbon neutrality lies in how China's central cities realize a low-carbon transition first.
(2)Cities with developed manufacturing sector
China Integrated City Index each year evaluates the manufacturing "radiance" strength of Chinese cities. The "radiance" strength is an indicator to gauge a city's overall influence, and the manufacturing "radiance" strength is the integrated evaluation of a city's exports and manufacturing industry.
As Figure 2 indicates, the top 30 manufacturing cities were Shenzhen, Suzhou, Dongguan, Shanghai, Ningbo, Foshan, Chengdu, Guangzhou, Wuxi, Hangzhou, Xiamen, Huizhou, Zhongshan, Qingdao, Tianjin, Beijing, Nanjing, Jiaxing, Jinhua, Zhengzhou, Zhuhai, Quanzhou, Shaoxing, Yantai, Changzhou, Xi'an, Taizhou, Nantong, Dalian, and Weihai. Among them, Shenzhen, Suzhou, Dongguan, Shanghai, Ningbo, Guangzhou, Wuxi, Hangzhou, Qingdao, Tianjin, Beijing, Nanjing, Zhengzhou, Xi'an, Taizhou, and Nantong made the list of the top 30 emitting cities. Except Zhengzhou and Xi'an, other cities are all located in the Yangtze River Delta, the Pearl River Delta, and the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region.
As the world's major industrial hubs for global supply chains, these manufacturing cities that are big exporters are also big emitters. Among the top 10 cities in terms of manufacturing, only Chengdu and Foshan didn't make the list of top 30 emitters, ranking 34th and 43rd, respectively.
The top 10 Chinese manufacturing cities accounted for 12.3% of China's total emissions, the top 30 accounted for 30.7%. Therefore, these Chinese manufacturing cities face an arduous task of achieving carbon neutrality.
Figure 2 Top 30 cities in terms of manufacturing in 2020
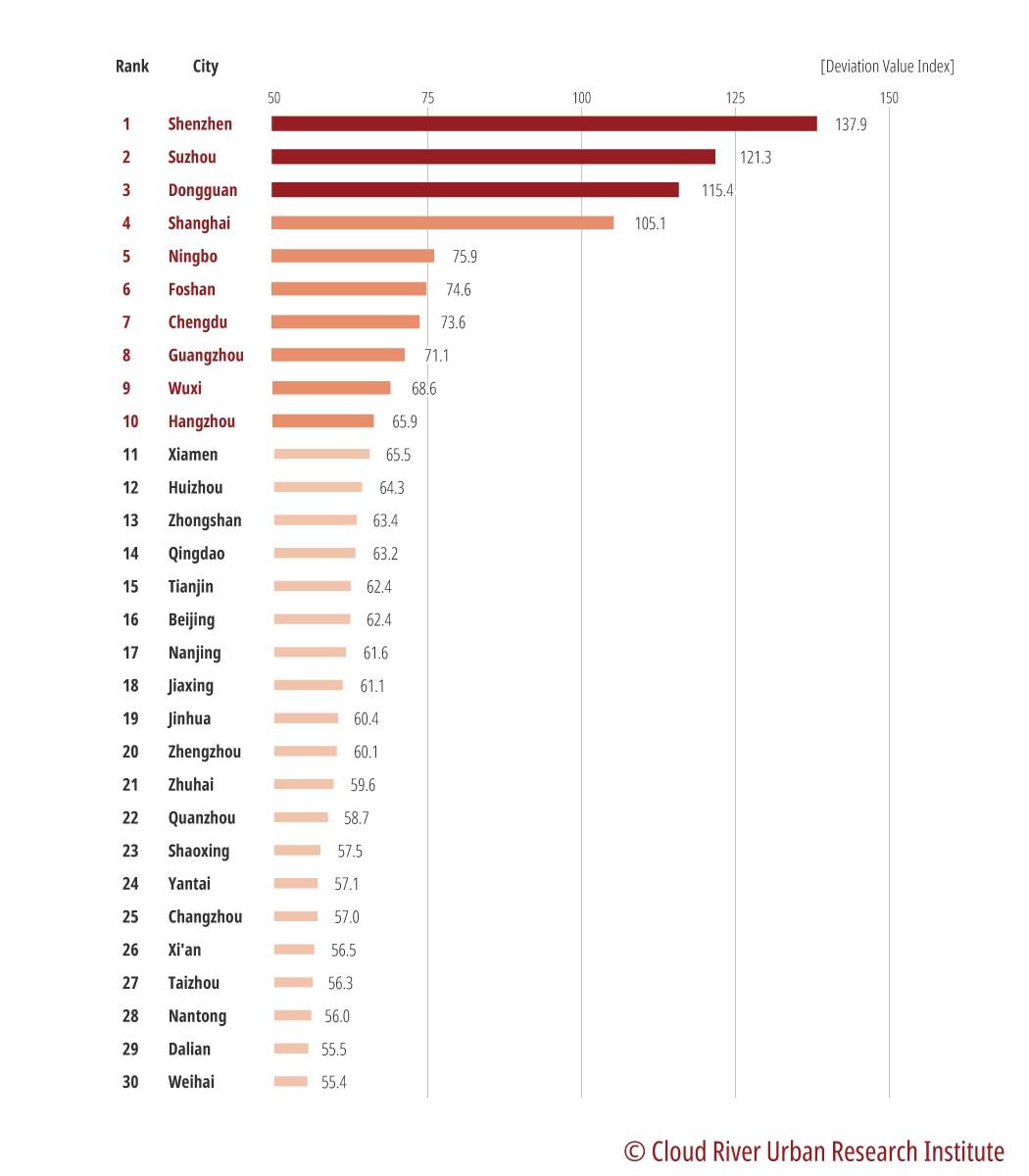
Source: China Integrated City Index 2020 by Cloud River Urban Research Institute
(3) Chinese cities with developed energy/heavy chemical industries
The top 30 Chinese cities by carbon emissions mostly have developed energy/heave chemical industries. This article is aimed to analyze and evaluate these cities based on the index of power generation.
Coal-fired power generation is the leading contributor to carbon emissions. China Integrated City Index uses the indicator of power generation to monitor and evaluate power generation in 297 cities at the prefecture level and above.
As Figure 3 indicates, the top 30 cities in terms of power generation were Yulin, Yichang, Ordos, Binzhou, Suzhou, Yinchuan, Shanghai, Jiaxing, Chongqing, Shenzhen, Fuzhou, Tianjin, Ningbo, Baotou, Yantai, Huainan, Lijiang, Chengdu, Tangshan, Liaocheng, Zhaotong, Yangjiang, Tongliao, Hohhot, Jining, Dalian, Xuzhou, Ningde, and Ya'an. Among them, 10 cities made the list of the top 30 emitting cities, namely ordos, Suzhou, Shanghai, Chongqing, Shenzhen, Tianjin, Ningbo, Tangshan, Hohhot, and Xuzhou, as these cities are also big emitters due to power generation.
Among the top 10 cities in terms of power generation, Yulin, Yichang, Binzhou, Yinchuan, and Jiaxing also made the list of top 100 emitters at 31st, 44th, 78th, and 84th places, respectively, while Yichang, a city that relies heavily on hydro power generation, doesn't emit much carbon dioxide, despite being a big power generator.
The top 10 Chinese emitting cities accounted for a combined 9% of the nation's total emissions, the top 30 accounted for a combined 20.9%. From this perspective, China's quick shift from its reliance on coal-fired power will be critical to the country's effort to realize carbon neutrality.
Figure 3 Top 30 Chinese cities in terms of power generation in 2020

Source: China Integrated City Index 2020 by Cloud River Urban Research Institute
3. Multiple steps taken to achieve carbon neutrality
From the analysis above, the top 30 emitters in the ranking included Shanghai, Tianjin, and Wuhan, which are populous central cities with developed manufacturing and energy/heavy chemical industries. The top 30 emitters included Shenzhen, Suzhou, Dongguan, Wuxi, Ningbo, Qingdao, and Nantong that have transformed into manufacturing hubs in a short period of time due to their strong exporting industries which can absorb huge populations. They also included Ordos, Zaozhuang, Hohhot and Xuzhou, which have developed into large power bases due to their rich coal resources, Daqing, which relies on petroleum resources to grow into a major petrochemical city, and Tangshan, the largest steel city in the world. The carbon dioxide emissions of Chinese cities are closely related with populations, living standards, urban structures, industrial structures and energy mix. Therefore, Chinese cities should take multiple steps to reach carbon peak and neutrality goals.
In terms of city structures, improving lifestyle, upgrading public transportation systems, enhancing the energy efficiency of buildings will be priorities for Chinese cities to reduce carbon reductions. How to solve problems that have been left in the rapid urbanization process will be the key to Chinese cities' high-quality development.
In terms of industrial structures, it is necessary to further improve the technological level, energy efficiency, and industrial structure of supercities with a strong manufacturing industry. At the same time, it is also necessary to accelerate the technological revolution of energy and heavy industries, such as electricity, steel and chemical industries, and strive for the realization of low or even zero emissions of energy and heavy chemical industries as soon as possible.
In terms of energy mix, it is necessary to change the energy mix that relies too much on coal resources as soon as possible and expedite the transformation to renewable energy.
It should be noted that energy conservation and emission reductions should not be seen as a negative measure to restrain the economy, but should be a new opportunity for high-quality development. New energy vehicles, batteries and other NEV-related industries have become new engines to drive China's industrial development. China accounts for more than 80% of the global output of the main links in the photovoltaic manufacturing, such as polysilicon, silicon wafers, cells and modules. China's installed capacity of renewable energy is growing rapidly, with its installed capacity of hydropower, wind power, and photovoltaic power generation all ranking first in the world.
It is a daunting task and challenge to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060, as Chinese cities need to grope for scientific paths to carbon neutrality, which entails wisdom and unremitting efforts.
(This article is an excerpt from Zhou Muzhi's paper "China's carbon emission structure from the perspective of cities: China is still growing while Japan, the U.S. and Europe have peaked," published in Issue 337 of the Journal of Tokyo Keizai University: Economics in 2023. Researchers at the Cloud River Urban Research Institute Kurimoto Kenichi, Zhen Xuehua, and Zhao Jian contributed to data compilation and graphic production in the article.)





